SuiteCloud Vietnam là Solution Partner top đầu của Oracle NetSuite tại Việt Nam
SuiteCloud Vietnam là Solution Partner top đầu của Oracle NetSuite tại Việt Nam
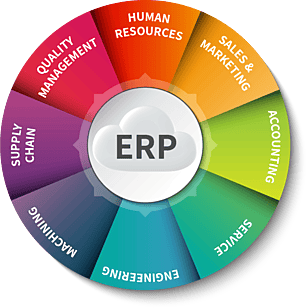
SuiteCloud Vietnam (PointStar Vietnam) là đối tác Top đầu của Oracle NetSuite tại Việt nam. Chúng tôi triển khai hệ thống Oracle NetSuite ERP là nền tảng quản trị hàng đầu thế giới, giúp doanh nghiệp tự động hóa quy trình Tài chính, Kế toán, CRM, Bán hàng, Cung ứng, Kho, Sản xuất và Báo cáo thông minh trên một hệ thống duy nhất. Với khả năng tích hợp linh hoạt, báo cáo phân tích đa chiều, toàn cảnh thời gian thực và mở rộng dễ dàng, Oracle NetSuite giúp doanh nghiệp nâng cao hiệu suất, tối ưu chi phí và ra quyết định nhanh chóng chính xác hơn.
40.000+
40.000+
Doanh nghiệp đang sử dụng Oracle NetSuite ERP
Doanh nghiệp đang sử dụng Oracle NetSuite ERP
2.689+
2.689+
Chức năng đáp ứng mọi yêu cầu của doanh nghiệp
Chức năng đáp ứng mọi nhu cầu của doanh nghiệp
100+
100+
Khách hàng đã được chúng tôi triển khai thành công
Khách hàng đã được chúng tôi triển khai thành công

















Chúng tôi triển khai Oracle NetSuite ERP cho nhiều ngành
Thành công của dự án triển khai ERP phụ thuộc vào năng lực kinh nghiệm và lực lượng chuyên gia của đối tác triển khai!
Vì sao chọn SuiteCloud Vietnam?
Vì sao chọn SuiteCloud Vietnam?
Chuyên sâu về Oracle NetSuite
SuiteCloud Vietnam là đối tác triển khai hàng đầu của hãng Oracle sở hữu đội ngũ nhiều chuyên gia giàu kinh nghiệm, am hiểu sâu về Oracle NetSuite ERP.
Kinh nghiệm triển khai đa ngành
Chúng tôi đã đồng hành cùng nhiều doanh nghiệp sản xuất, thương mại, dịch vụ, phân phối và giúp họ tối ưu hóa vận hành, nâng cao hiệu suất.
Tư vấn & Triển khai linh hoạt
Mỗi doanh nghiệp có nhu cầu riêng, chúng tôi tùy chỉnh giải pháp phù hợp, giúp triển khai hiệu quả, tiết kiệm chi phí và đảm bảo thành công.
Hỗ trợ tận tâm, đồng hành lâu dài
Không chỉ triển khai, chúng tôi cam kết hỗ trợ sau golive, đào tạo đội ngũ, cập nhật công nghệ và tối ưu hệ thống để doanh nghiệp khai thác tối đa giá trị từ hệ thống.

Chuyên sâu về
Oracle NetSuite
SuiteCloud Vietnam là đối tác triển khai hàng đầu của hãng Oracle, sở hữu đội ngũ chuyên gia giàu kinh nghiệm, am hiểu sâu về Oracle NetSuite ERP.

Kinh nghiệm triển khai đa ngành
Chúng tôi đã đồng hành cùng nhiều doanh nghiệp sản xuất, thương mại, dịch vụ, phân phối và giúp họ tối ưu hóa vận hành, nâng cao hiệu suất.

Tư vấn & Triển khai linh hoạt
Mỗi doanh nghiệp có nhu cầu riêng, chúng tôi tùy chỉnh giải pháp phù hợp, giúp triển khai hiệu quả, tiết kiệm chi phí và đảm bảo thành công.

Hỗ trợ tận tâm, đồng hành lâu dài
Không chỉ triển khai, chúng tôi cam kết hỗ trợ sau golive, đào tạo đội ngũ, cập nhật công nghệ và tối ưu hệ thống để doanh nghiệp khai thác tối đa giá trị từ hệ thống.